Understanding Fidelity Loan Calculators
Fidelity loan calculators are powerful tools designed to help you quickly estimate the costs and terms associated with various loan products. Understanding how these calculators work can empower you to make informed financial decisions, whether you’re planning a home renovation, consolidating debt, or financing a significant purchase. This guide will break down the functionality and benefits of using these essential financial planning tools.
Purpose of Fidelity Loan Calculators
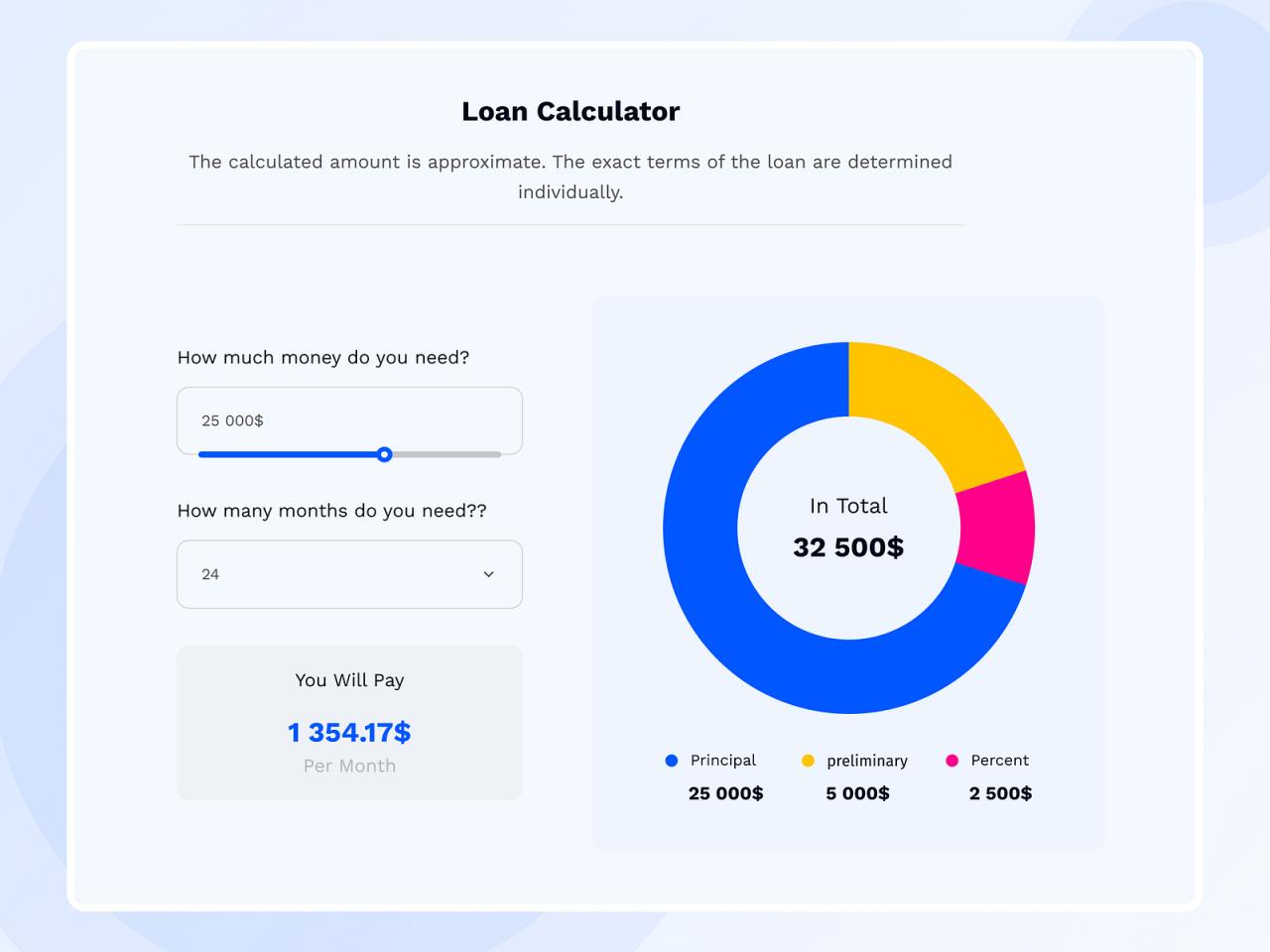
The primary purpose of a fidelity loan calculator is to provide users with a rapid and accurate estimate of loan payments, total interest paid, and the overall cost of borrowing. By inputting key details such as loan amount, interest rate, and loan term, the calculator performs the necessary computations, presenting the results in a clear and concise format. This allows users to compare different loan options and make well-informed decisions aligned with their financial goals and capabilities. This avoids the time and effort of manual calculations, which can be complex and prone to errors.
Types of Loans Handled by Fidelity Loan Calculators
Fidelity loan calculators typically handle a range of loan types, though the specific offerings can vary depending on the platform. Common examples include:
- Personal Loans: These are unsecured loans used for various purposes, offering flexible terms and repayment options.
- Home Equity Loans: These loans use your home’s equity as collateral, often resulting in lower interest rates than unsecured loans.
- Auto Loans: Used to finance the purchase of a vehicle, these loans typically have fixed interest rates and terms.
- Student Loans: These loans are designed to help finance education expenses, with varying repayment plans and interest rates.
It’s crucial to note that not all fidelity loan calculators will support all loan types. Always verify the calculator’s capabilities before using it.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Fidelity Loan Calculator
Using a fidelity loan calculator is generally straightforward. Most follow a similar process:
- Select Loan Type: Choose the type of loan you are interested in from the available options (e.g., personal loan, auto loan).
- Enter Loan Amount: Input the total amount you wish to borrow.
- Enter Interest Rate: Specify the annual interest rate offered by the lender. This is often expressed as a percentage.
- Enter Loan Term: Indicate the loan’s duration, usually expressed in months or years.
- Input Additional Fees (if applicable): Some calculators allow you to include additional fees, such as origination fees or closing costs, for a more comprehensive estimate.
- Review Results: The calculator will display your estimated monthly payment, total interest paid over the loan’s lifetime, and the total amount repaid.
Remember that the results are estimates. Always confirm the final terms with the lender before proceeding with the loan.
Comparison of Fidelity Loan Calculator Features
The features and capabilities of fidelity loan calculators can vary. The following table highlights some key differences:
| Loan Type | Interest Rate Calculation Method | Fee Inclusion | Additional Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Personal, Auto, Home Equity | Simple Interest, Compound Interest | Yes/No | Amortization Schedule, Payment Comparison Tool |
| Personal, Student | Compound Interest | Yes | Debt Consolidation Calculator, Prepayment Options |
| Home Equity | Simple Interest | No | Tax Deductibility Estimator |
| Auto | Compound Interest | Yes | Trade-in Value Calculator |
Key Features and Functionality
Fidelity’s loan calculator, like any powerful financial tool, hinges on its ability to accurately and efficiently process key information to provide users with a clear picture of their potential loan obligations. Understanding its core features and how it handles calculations is crucial for making informed borrowing decisions. This section will delve into the essential input parameters, the calculator’s handling of different interest rate types, and the methods used to generate critical loan data.
Fidelity loan calculator – The accuracy of the output depends entirely on the accuracy of the input. Garbage in, garbage out, as the saying goes. Therefore, it’s vital to understand what data the calculator requires and how to provide it correctly.
Essential Input Parameters
The Fidelity loan calculator requires several key inputs to generate a comprehensive loan analysis. These include: the loan amount (the principal sum borrowed), the annual interest rate (the cost of borrowing, expressed as a percentage), and the loan term (the length of the loan, typically expressed in months or years). Additionally, you might need to specify the loan type (e.g., mortgage, personal loan), as this can influence the calculation process. Providing accurate and complete information in these fields is critical for obtaining reliable results. Inaccurate data will lead to inaccurate projections. For instance, entering a loan amount of $100,000 with a 5% interest rate over 30 years will yield a significantly different result than entering $50,000 with the same interest rate and term.
Interest Rate Handling: Fixed vs. Variable
A crucial aspect of any loan calculator is its ability to handle different interest rate types. Fidelity’s calculator likely differentiates between fixed and variable interest rates. A fixed interest rate remains constant throughout the loan’s term, making it easier to predict future payments. A variable interest rate, however, fluctuates based on market conditions, introducing an element of uncertainty. The calculator will use different calculation methods depending on the chosen interest rate type. For fixed rates, the calculation is straightforward, using a constant interest rate throughout the amortization schedule. Variable rates require more complex calculations, often incorporating projections or historical data to estimate future interest rates. For example, a variable rate loan might start with a 4% interest rate but could increase to 5% or decrease to 3% over the life of the loan, impacting the monthly payment and total interest paid.
Calculation Methods: Monthly Payments, Total Interest, and Amortization Schedule
The calculator employs standard financial formulas to determine key loan metrics. Monthly payments are typically calculated using the following formula:
M = P [ i(1 + i)^n ] / [ (1 + i)^n – 1]
Where:
M = Monthly Payment
P = Loan Amount (Principal)
i = Monthly Interest Rate (Annual Interest Rate / 12)
n = Total Number of Months (Loan Term in Years * 12)
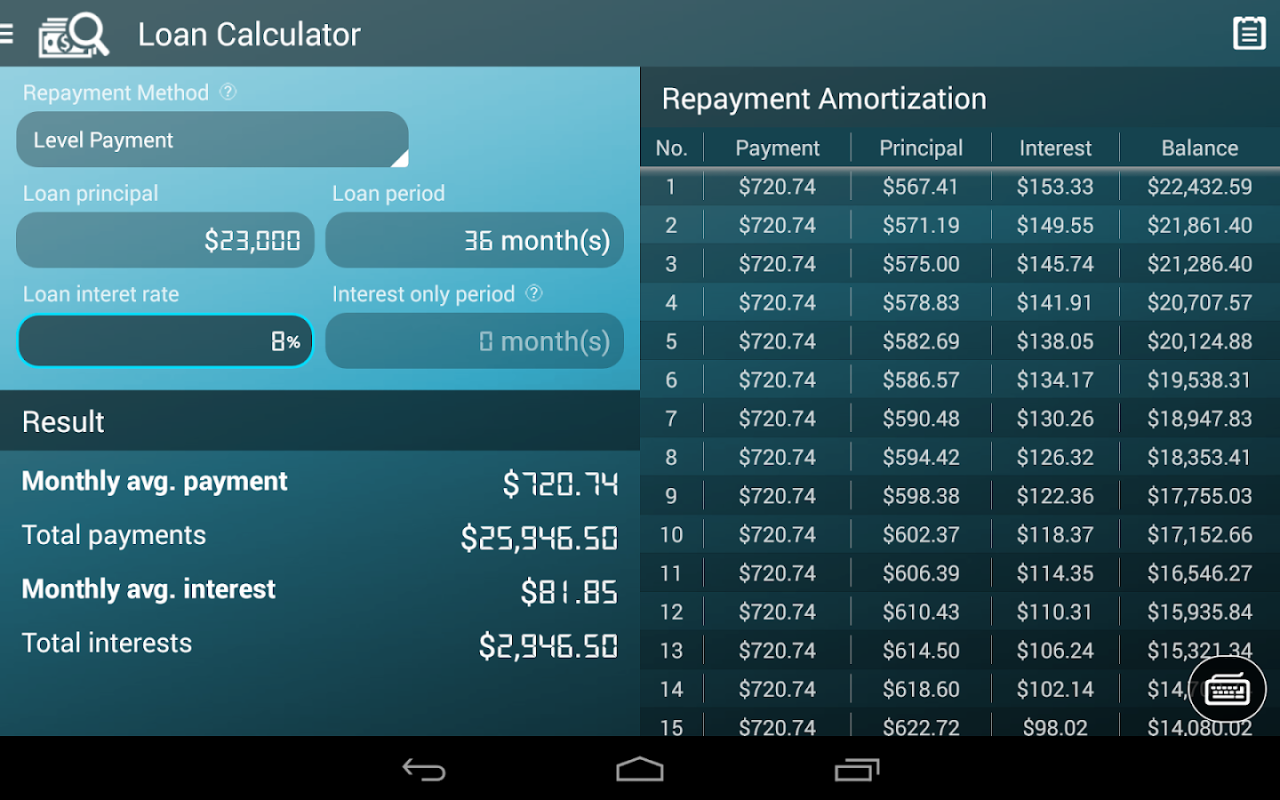
Total interest paid is simply the total amount repaid minus the principal loan amount. The amortization schedule, a crucial feature, breaks down each payment into the portion allocated to principal and interest over the loan’s lifetime. This schedule provides a detailed timeline of how the loan is repaid, illustrating how the proportion of principal to interest changes over time.
Sample Loan Amortization Schedule
Understanding an amortization schedule is key to grasping your loan repayment. Here’s a simplified example illustrating the breakdown of payments over time:
This example shows a $10,000 loan at a 5% annual interest rate over 3 years (36 months).
- Month 1: Payment: $304.22; Principal: $208.22; Interest: $96.00
- Month 6: Payment: $304.22; Principal: $234.61; Interest: $69.61
- Month 12: Payment: $304.22; Principal: $263.34; Interest: $40.88
- Month 36: Payment: $304.22; Principal: $304.22; Interest: $0.00
Notice how the proportion of the payment going towards principal increases over time while the interest portion decreases. This is a standard characteristic of loan amortization.
Factors Affecting Loan Calculations
Understanding the intricacies of loan calculations is crucial for making informed financial decisions. Several key factors significantly impact the total cost of your loan and your monthly payments. Ignoring these factors can lead to unexpected expenses and financial strain. This section will dissect these critical elements, providing you with a clear understanding of their influence.
Interest Rate Impact on Loan Cost, Fidelity loan calculator
The interest rate is arguably the most significant factor determining the overall cost of a loan. A higher interest rate translates directly into higher monthly payments and a substantially larger total interest paid over the life of the loan. Conversely, a lower interest rate reduces both monthly payments and the total interest paid. For example, a $200,000 loan at 5% interest over 30 years will result in significantly lower total interest paid compared to the same loan at 7% interest. The difference can amount to tens of thousands of dollars over the loan’s duration. This underscores the importance of securing the most favorable interest rate possible.
Loan Term’s Influence on Monthly Payments and Total Interest
The loan term, or repayment period, also plays a crucial role. Shorter loan terms lead to higher monthly payments but lower total interest paid because the principal is repaid faster. Longer loan terms result in lower monthly payments but significantly higher total interest paid over the life of the loan. Consider a $100,000 loan: a 15-year term will have higher monthly payments but less total interest compared to a 30-year term, which will have lower monthly payments but substantially more interest paid. The choice depends on your financial capacity and long-term goals.
Loan Amount’s Effect on Overall Loan Cost
The principal loan amount, or the initial sum borrowed, directly influences the overall cost. A larger loan amount will naturally lead to higher monthly payments and a greater total interest paid, while a smaller loan amount results in lower monthly payments and less total interest. This is a straightforward relationship: the more you borrow, the more you’ll pay back, both in principal and interest.
Comparative Analysis of Loan Factors
The interplay of these factors can be complex. The following table illustrates the impact of varying interest rates, loan terms, and loan amounts on monthly payments and total interest paid. These figures are illustrative and should not be considered financial advice. Always consult with a financial professional for personalized guidance.
| Loan Amount | Interest Rate | Loan Term (Years) | Approximate Monthly Payment | Approximate Total Interest Paid |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| $150,000 | 4% | 15 | $1,100 | $36,000 |
| $150,000 | 6% | 15 | $1,250 | $56,000 |
| $150,000 | 4% | 30 | $720 | $120,000 |
| $200,000 | 4% | 30 | $960 | $160,000 |
Practical Applications and Examples: Fidelity Loan Calculator
Fidelity loan calculators, while seemingly simple tools, offer significant advantages in various financial scenarios. Understanding their application can dramatically improve your financial decision-making process, leading to better budgeting and smarter borrowing. This section will explore practical examples to illustrate the calculator’s power and utility.
A fidelity loan calculator’s primary benefit lies in its ability to provide a clear, concise picture of loan repayment. This allows you to compare different loan offers effectively and make informed choices based on your financial capabilities and long-term goals. It’s not just about the interest rate; it’s about the complete financial picture.
Real-World Scenarios and Benefits
The calculator’s usefulness extends beyond simple loan comparisons. For instance, consider someone planning a home renovation. They might receive multiple loan offers with varying interest rates, terms, and fees. By inputting the details of each offer into the calculator, they can instantly compare the total cost, monthly payments, and overall interest paid. This allows for a rational choice based on their budget and repayment capacity, rather than simply focusing on the lowest advertised interest rate. Similarly, a business owner considering expansion could use the calculator to evaluate the financial implications of different loan options, ensuring the expansion aligns with their financial health.
Financial Planning and Budgeting Assistance
Integrating a fidelity loan calculator into your financial planning is crucial. By inputting projected income and expenses, you can determine the maximum loan amount you can comfortably afford without jeopardizing your financial stability. This prevents over-borrowing and the potential stress of excessive debt. The calculator helps you build a realistic budget that incorporates loan repayments, ensuring you avoid financial pitfalls. This proactive approach promotes responsible borrowing and enhances your overall financial well-being.
Hypothetical Loan Scenario and Repayment Schedule
Let’s imagine Sarah needs a $20,000 loan for a new car. She finds two offers: one with a 5% interest rate over 60 months and another with a 7% interest rate over 48 months. Using a fidelity loan calculator, she inputs the loan amount, interest rate, and loan term for each offer. The calculator will then generate detailed repayment schedules for both options, showing the monthly payment, total interest paid, and the total amount repaid over the life of the loan. This allows Sarah to compare the total cost of each loan and choose the option that best aligns with her budget and financial goals. For example, the calculator might show that the 5% loan, despite having a longer term, results in a lower total interest paid compared to the shorter-term, higher-interest loan.
Comparing Loan Offers
A fidelity loan calculator empowers consumers to make informed comparisons between different loan offers. It presents a comprehensive view, moving beyond the superficial allure of low interest rates to reveal the total cost of borrowing. By inputting details such as loan amount, interest rate, loan term, and any associated fees, the calculator generates a detailed comparison of monthly payments, total interest paid, and the overall cost of each loan. This allows for a side-by-side comparison, highlighting the key differences and enabling a rational decision-based on individual financial circumstances. This data-driven approach ensures that borrowers choose the most suitable loan, minimizing financial risk and maximizing long-term financial health.
Limitations and Considerations
While Fidelity’s loan calculator offers a valuable tool for estimating loan payments and exploring different loan scenarios, it’s crucial to understand its limitations. Relying solely on the calculator’s output without considering other factors can lead to inaccurate financial planning and potentially costly mistakes. Remember, this tool provides estimates, not guarantees.
Using a loan calculator like Fidelity’s provides a helpful starting point, but it’s not a substitute for comprehensive financial planning. Several crucial aspects of borrowing money are often not explicitly factored into these simplified calculations. Ignoring these factors can lead to significant discrepancies between the projected costs and the actual expenses you’ll incur.
Excluded Financial Factors
Standard loan calculators, including Fidelity’s, often omit several key costs associated with borrowing. These overlooked expenses can significantly impact your overall loan costs. For example, closing costs, which can include appraisal fees, title insurance, and other administrative charges, are rarely incorporated into initial loan estimations. Prepayment penalties, levied if you pay off your loan early, are another frequently omitted factor. These penalties can range from a small percentage of the remaining balance to several months’ worth of interest, significantly altering your overall financial picture. Finally, the calculator usually doesn’t factor in potential changes in interest rates over the life of the loan.
Importance of Financial Advisor Consultation
Before committing to any significant financial decision, such as taking out a substantial loan, consulting with a qualified financial advisor is paramount. A financial advisor can provide personalized guidance based on your individual financial situation, risk tolerance, and long-term goals. They can help you understand the complete financial picture, including factors beyond the scope of a loan calculator, ensuring you make informed decisions aligned with your overall financial well-being. They can also help navigate complex financial products and ensure you’re getting the best possible terms for your loan. This professional consultation can prevent costly errors and help you achieve your financial objectives more effectively.
Additional Factors to Consider
It’s essential to go beyond the calculator’s output and consider several additional factors before finalizing a loan agreement. This holistic approach ensures a realistic understanding of your financial obligations.
- Your Current Debt Load: Assess your existing debts (credit cards, student loans, etc.) and how a new loan will affect your overall debt-to-income ratio. A high debt-to-income ratio can impact your credit score and limit your borrowing options in the future.
- Emergency Fund: Do you have sufficient savings to cover unexpected expenses? Unexpected events can significantly strain your finances, making loan repayment more challenging. A robust emergency fund acts as a buffer against unforeseen circumstances.
- Interest Rate Fluctuations: Understand that interest rates can change over time. While the calculator uses a current rate, this might not reflect future rates. Consider scenarios with slightly higher interest rates to account for potential increases.
- Loan Term Length: A longer loan term reduces monthly payments, but it increases the total interest paid over the life of the loan. Conversely, a shorter term increases monthly payments but lowers the overall interest cost. Carefully weigh the trade-offs.
- Hidden Fees: Always thoroughly review the loan agreement for any additional fees beyond those explicitly mentioned. These can include origination fees, late payment fees, and other charges that can significantly add to the overall cost.