Understanding 365/360-Day Loan Calculations
Choosing the right loan calculator is crucial for accurate financial planning. A seemingly small detail like the number of days in a year—365 or 360—can significantly impact your loan’s total cost. This difference stems from the calculation methods used to determine daily interest rates and ultimately, the total amount you repay. Understanding these nuances is key to making informed borrowing decisions.
Understanding the difference between 365-day and 360-day year loan calculations is vital for accurate financial projections. The choice between these methods directly affects the daily interest rate applied to your loan, ultimately influencing the total interest accrued over the loan’s term.
365-Day vs. 360-Day Year Calculations
The core difference lies in the denominator used when calculating the daily interest rate. In a 365-day calculation, the annual interest rate is divided by 365 to determine the daily rate. Conversely, a 360-day calculation divides the annual interest rate by 360. This seemingly small difference of five days can lead to noticeable variations in the total interest paid, especially on larger loans or longer repayment periods. The 360-day method, also known as the “banker’s year,” simplifies calculations, although it results in slightly higher interest payments for the borrower.
Impact on Interest Calculation, 365/360 commercial loan calculator
The impact on interest calculation is straightforward: a 360-day year results in a slightly higher daily interest rate compared to a 365-day year. This is because the annual interest is spread over fewer days. Consequently, the total interest accrued over the loan term will be higher with the 360-day method. The formula for calculating simple interest further illustrates this:
Simple Interest = Principal x Interest Rate x Time
Where “Time” is expressed as a fraction of the year. Using a 360-day year effectively increases the “Time” fraction, thus increasing the total interest.
Loan Scenarios Illustrating Differences
Let’s examine the differences using specific loan scenarios. The following table illustrates how the choice between a 365-day and a 360-day calculation can impact the final loan amount. These figures are calculated using simple interest for illustrative purposes. More complex loan structures might involve compounding interest, which would further amplify the differences.
| Loan Amount | Interest Rate | 365-Day Total | 360-Day Total |
|---|---|---|---|
| $10,000 | 5% (Annual) | $10,500.00 | $10,508.33 |
| $50,000 | 8% (Annual) | $54,000.00 | $54,166.67 |
| $100,000 | 10% (Annual) | $110,000.00 | $110,833.33 |
Note: These calculations assume a one-year loan term for simplicity. The differences would be more pronounced with longer loan terms.
Commercial Loan Calculator Features
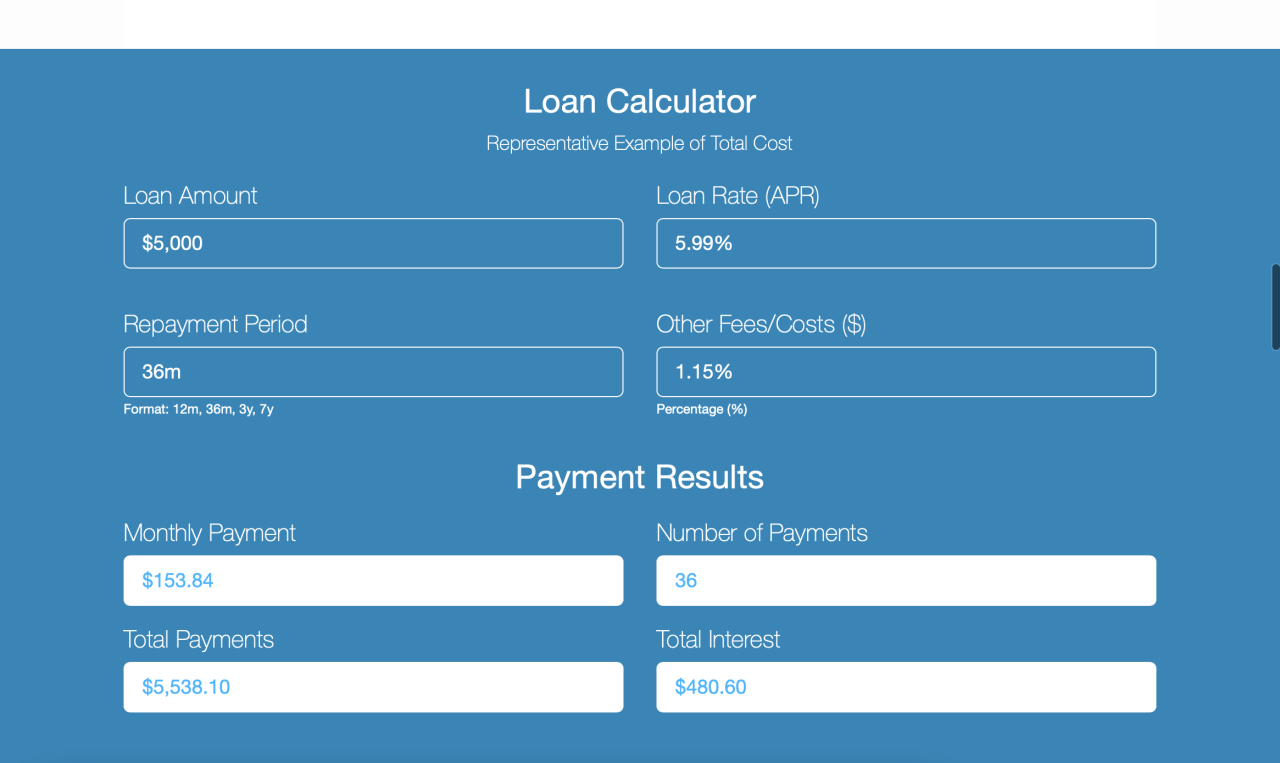
A robust commercial loan calculator is more than just a simple interest calculation tool; it’s a powerful decision-making instrument for businesses navigating the complexities of financing. The right features empower users with accurate, insightful data, facilitating informed choices regarding their borrowing needs. This leads to better financial planning and ultimately, stronger business outcomes.
The core functionality revolves around providing users with a clear and precise understanding of their loan repayment obligations. This requires a sophisticated calculation engine, but also a user-friendly interface that simplifies complex financial concepts.
Essential Features of a Robust Commercial Loan Calculator
A truly effective commercial loan calculator must include several key features to be useful and reliable. These features ensure the calculator provides comprehensive and accurate results, facilitating informed financial decisions. Omitting any of these critical components would significantly diminish the calculator’s value and accuracy.
- Loan Amount: This field allows the user to input the principal amount they intend to borrow. Accurate input is crucial for all subsequent calculations.
- Interest Rate: This field accepts the annual interest rate offered by the lender. The calculator should handle various input formats (e.g., percentage, decimal). Clear instructions on input format are essential.
- Loan Term: This field specifies the duration of the loan, typically expressed in years or months. The calculator should accommodate various input units and convert them consistently to a standardized format for calculations.
- Payment Frequency: This critical field defines how often loan payments are made (e.g., monthly, quarterly, annually). The calculator must accurately adjust calculations based on this selection.
- 365/360 Day-Count Convention Selection: This allows the user to choose between the 365-day and 360-day methods for calculating interest, providing flexibility for various loan agreements.
- Amortization Schedule Generation: This feature displays a detailed breakdown of each payment, showing the principal and interest components. This provides transparency and helps users understand their repayment schedule.
- Total Interest Paid: The calculator should clearly display the total interest payable over the loan’s lifespan.
- Total Payment Amount: The sum of all payments, including principal and interest, should be readily available.
User Interface Flow for a 365/360 Commercial Loan Calculator
Intuitive design is paramount. A poorly designed interface can confuse users and lead to errors in input, resulting in inaccurate calculations. A clear and logical flow ensures a positive user experience, leading to greater adoption and trust in the calculator’s results.
The ideal user flow would begin with a concise and visually appealing introduction explaining the calculator’s purpose and functionality. Following this, the input fields should be clearly labeled and logically grouped. Consider a vertical layout, with each field presented sequentially, starting with loan amount, then interest rate, loan term, and payment frequency. The 365/360 day-count convention selection should be prominently displayed, possibly as a radio button selection.
Upon inputting all necessary data, a prominent “Calculate” button should initiate the computation. The results should be displayed clearly, ideally in a tabular format for the amortization schedule, with total interest and total payment amounts highlighted. Consider incorporating visual aids like charts or graphs to further enhance understanding. Finally, a clear “Reset” button should allow users to easily clear the fields and perform new calculations. The entire process should be quick, efficient, and visually appealing, promoting user engagement and confidence in the results.
Impact of Interest Rate and Loan Term

Understanding the interplay between interest rates, loan terms, and the ultimate cost of borrowing is crucial for any business. Both the 365-day and 360-day calculation methods impact the final repayment amount, but their differences become more pronounced with varying interest rates and loan durations. This section will delve into the specifics of these impacts, illustrating how seemingly small changes can significantly affect your bottom line.
The relationship between the interest rate and the total loan cost is directly proportional. Higher interest rates lead to higher total interest payments, regardless of whether a 365-day or 360-day year is used. However, the 360-day method, due to its slightly shorter year, generally results in slightly lower total interest costs compared to the 365-day method for the same interest rate and loan term. This difference, while seemingly small on a percentage basis, can accumulate to a noticeable amount over longer loan terms.
Interest Rate’s Influence on Total Loan Cost
A 1% increase in the interest rate on a $100,000 loan can result in thousands of dollars more in interest payments over the life of the loan. For example, a 5% interest rate on a five-year loan might result in a total interest payment of $12,000 using the 365-day method, while the same loan with a 6% interest rate could lead to over $15,000 in interest. The difference is even more pronounced with longer loan terms. The 360-day method would show a slightly lower total interest cost in both scenarios, but the relative difference between the 5% and 6% scenarios would remain similar. This demonstrates the significant impact of even small interest rate fluctuations on the overall cost.
Loan Term’s Effect on Final Repayment
Longer loan terms generally result in lower monthly payments, but significantly higher total interest payments. This is because you are paying interest over a longer period. Consider a $100,000 loan at a 5% interest rate. A short-term loan (e.g., 1 year) will have high monthly payments but relatively low total interest. A long-term loan (e.g., 10 years) will have lower monthly payments, but the total interest paid will be substantially higher. The difference in total repayment between the 365-day and 360-day methods becomes more noticeable as the loan term lengthens.
Visual Representation of Interest Rate and Loan Term Impacts
Imagine a graph with the x-axis representing loan terms (in years) ranging from 1 to 10 years, and the y-axis representing the total loan cost. Two lines are plotted: one for the 365-day calculation method and one for the 360-day method. Each line would have multiple data points representing the total cost at various interest rates (e.g., 4%, 5%, 6%). The graph would clearly show that for both calculation methods, the total loan cost increases with longer loan terms and higher interest rates. Furthermore, the 360-day method line would consistently lie slightly below the 365-day method line, indicating lower total costs for the 360-day calculation across all loan terms and interest rates. The difference between the lines would become more pronounced as the loan term increases, illustrating the compounding effect of the slightly shorter year in the 360-day calculation.
Advanced Calculator Features

Our 365/360 commercial loan calculator isn’t just about basic calculations; it’s designed to provide you with a comprehensive financial picture. This section delves into the advanced features that empower you to make informed decisions, offering insights beyond simple interest and principal calculations. We’ll explore how the calculator generates detailed amortization schedules and handles complexities like balloon payments and variable interest rates.
365/360 commercial loan calculator – Understanding these advanced features is crucial for accurately projecting loan repayments and managing your financial obligations effectively. The ability to model different scenarios allows for proactive financial planning and strategic decision-making.
Amortization Schedule Generation
The calculator generates a detailed amortization schedule, breaking down each payment into its principal and interest components. This schedule provides a clear, month-by-month visualization of how your loan balance decreases over time. This transparency is vital for budgeting and understanding the true cost of borrowing.
The schedule is presented in a user-friendly HTML table, making it easy to download and analyze. The information is organized for optimal readability and clarity, enabling quick comprehension of your loan repayment trajectory. The table’s responsive design ensures optimal viewing across different devices.
| Payment Number | Payment Amount | Principal Paid | Interest Paid |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | $1,000 | $100 | $900 |
| 2 | $1,000 | $105 | $895 |
| 3 | $1,000 | $110 | $890 |
Balloon Payment Functionality
A balloon payment is a large, lump-sum payment due at the end of a loan term. Our calculator allows you to incorporate balloon payments into your calculations, providing a realistic projection of your total repayment obligations. This feature is particularly useful for understanding the financial implications of loans structured with this type of payment.
By inputting the balloon payment amount and its due date, the calculator adjusts the amortization schedule accordingly, reflecting the impact of this final, larger payment on your monthly installments and overall loan cost. This allows for a comprehensive financial assessment of such loan structures.
Variable Interest Rate Calculations
Unlike fixed-rate loans, variable-rate loans have interest rates that fluctuate over time, often based on an index rate. Our calculator handles variable interest rates by allowing you to input a range of potential future interest rates or a specific schedule of rate changes.
This functionality is crucial for assessing the risk associated with variable-rate loans. By modeling different interest rate scenarios, you can estimate the potential impact of rate increases on your monthly payments and overall loan cost. This allows for a more comprehensive risk assessment before committing to a loan.
Understanding the potential impact of variable interest rates is vital for managing financial risk effectively.
Error Handling and Validation: 365/360 Commercial Loan Calculator
Robust error handling and input validation are crucial for a user-friendly and reliable 365/360 commercial loan calculator. Without these safeguards, incorrect inputs could lead to inaccurate calculations and potentially costly mistakes. A well-designed error-handling system guides users towards correct input, preventing frustration and ensuring the calculator’s accuracy.
This section details the methods employed to handle invalid user inputs and provides examples of the error messages displayed. We also Artikel the specific validation rules implemented for each input field. This ensures data integrity and a seamless user experience.
Invalid Input Handling Methods
The calculator employs several methods to handle invalid user inputs. First, it uses JavaScript to perform real-time validation. This means users receive immediate feedback as they type, preventing the submission of obviously incorrect data. For example, if a user enters text into a numerical field, an error message will appear instantly. If the validation fails, the form submission is blocked, preventing the calculation from proceeding with faulty data. Second, server-side validation provides an additional layer of security, checking the data again before processing it. This protects against any potential vulnerabilities or attempts to bypass client-side validation. Server-side validation also allows for more complex checks, such as verifying that the loan amount is within a reasonable range.
Error Message Examples
Clear and concise error messages are essential for guiding users. Here are a few examples:
* “Please enter a numeric value for the loan amount.” This message appears if a user enters text or special characters into the loan amount field.
* “The interest rate must be between 0% and 100%.” This message is shown if the entered interest rate falls outside the acceptable range.
* “The loan term must be a positive integer.” This message indicates an invalid entry in the loan term field (e.g., negative numbers or decimals).
* “Please select a valid repayment frequency.” This appears if the user doesn’t select a valid option from the dropdown menu for repayment frequency.
Input Validation Rules
The following input validation rules are applied to each field in the calculator to ensure data integrity:
- Loan Amount: Must be a positive numeric value. Must be within a reasonable range (e.g., $1,000 – $100,000,000).
- Interest Rate: Must be a numeric value between 0 and 100 (representing a percentage).
- Loan Term: Must be a positive integer representing the number of months or years, depending on the selected repayment frequency.
- Repayment Frequency: Must be selected from a predefined list of valid options (e.g., Monthly, Quarterly, Annually).
- Start Date: Must be a valid date in the past or present. Future dates might be disallowed depending on the application’s logic.
These rules ensure that only valid data is accepted by the calculator, preventing unexpected errors and providing a smooth user experience. The combination of real-time client-side and server-side validation significantly enhances the calculator’s reliability and usability. For example, imagine a scenario where a user accidentally enters a negative loan amount. The immediate error message prevents the user from proceeding with an invalid calculation, saving time and preventing potential confusion.
Comparison with Other Loan Calculators
Understanding the nuances of a 365/360-day commercial loan calculator requires comparing it to other loan calculators commonly used for different purposes. While all calculators compute loan payments, interest, and amortization schedules, significant differences exist in their features and underlying calculations, catering to specific loan types and user needs. This comparison will highlight these key distinctions.
The core difference lies in the day-count convention. While personal and mortgage loan calculators typically use a 365-day year (or sometimes 360 for simplicity), commercial loans frequently employ the 365/360 method, impacting the precise calculation of accrued interest. This seemingly small difference can significantly affect the total interest paid over the loan’s lifespan, especially for larger loans. Further distinctions arise from the complexities inherent in commercial lending, such as balloon payments, variable interest rates, and more sophisticated amortization schedules.
Feature Comparison of Loan Calculators
The following table compares the key features of a 365/360 commercial loan calculator with those designed for personal and mortgage loans. Note that specific features can vary depending on the individual calculator’s design and sophistication.
| Feature | 365/360 Commercial Loan Calculator | Personal Loan Calculator | Mortgage Loan Calculator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Day-Count Convention | 365/360 (or 360/360) | Typically 365 | Typically 365 or 360 |
| Interest Calculation Method | Precise calculation based on the 365/360 method, often incorporating daily compounding | Simple or compound interest, typically annual | Usually compound interest, typically monthly or annual |
| Loan Types Supported | Term loans, lines of credit, balloon payments, variable interest rates | Fixed-rate installment loans, personal lines of credit | Fixed-rate and adjustable-rate mortgages, various amortization schedules |
| Advanced Features | Often includes features for irregular payments, prepayments, and complex amortization schedules | Typically simpler, focusing on basic calculations | Often includes features for points, escrow, property taxes, and insurance |
| Amortization Schedule Detail | Detailed schedule showing daily or monthly interest accrual and principal payments | Monthly payment schedule | Monthly payment schedule with options for detailed breakdown |
| Output | Total interest paid, total payments, monthly payment, amortization schedule, and other relevant financial metrics | Total interest paid, monthly payment, total payments | Total interest paid, monthly payment, total payments, amortization schedule, principal and interest breakdown |
For instance, a $1 million commercial loan calculated using the 365/360 method over 10 years at 5% interest will yield a slightly different total interest and monthly payment compared to the same calculation using a standard 365-day year. This difference, while potentially small on a percentage basis, becomes substantial in the context of large commercial loans.